Overview
Sever?s Disease (calcaneal aphophysitis) is not really a disease, but more a repetitious strain injury. This is the most common cause of kids heel pain seen at Podiatry Care. Active children in football, soccer, basketball, netball and tennis with this type of foot pain complain of pain in the region of the heel bone particularly after exercise. In severe cases, children will complain of pain during exercise as well. It is a frequent cause of heel pain in children, particularly in the very active child. It is most often seen in children between the ages of 8 to 15 years as the growth plate is not fully developed or calcified at this time.
Causes
Sever?s disease is most likely to occur during the growth spurt that occurs in adolescence. For girls, growth spurts usually occurs between 8 and 13 years of age. For boys, it?s typically between 10 and 15 years of age. The back of the heel hardens and becomes stronger when it finishes growing, which is why Sever?s rarely occurs in older adolescents and teenagers.
Symptoms
Sever's Disease is most commonly seen in physically active girls and boys from ages 10 to 15 years old. These are the years when the growth plate is still ""open,"" and has not fused into mature bone. Also, these are the years when the growth plate is most vulnerable to overuse injuries, which are usually caused by sports activities. The most common symptoms of this disease include. Heel pain in one or both heels. Usually seen in physically active children, especially at the beginning of a new sports season. The pain is usually experienced at the back of the heel, and includes the following areas. The back of the heel (that area which rubs against the back of the shoe). The sides of the heel. Actually, this is one of the diagnostic tests for Sever's Disease, squeezing the rear portion of the heel from both sides at the same time will produce pain. It is known as the Squeeze Test.
Diagnosis
A Podiatrist can easily evaluate your child?s foot, lower limbs and muscular flexibility, to identify if a problem exists. If a problem is identified, a simple treatment plan is put in place. Initial treatment may involve using temporary padding and strapping to control motion or to cushion the painful area and based on the success of this treatment, a long-term treatment plan will be put in place. This long-term treatment plan may or may not involve Foot Supports, Heel Raises, muscle stretching and or strengthening.
Non Surgical Treatment
Sever?s disease treatment should be based on eliminating pain and restoring normal foot and leg biomechanics. As with most soft tissue injuries the initial treatment is Rest, Ice, and Protect. In the early phase you?ll most likely be unable to walk pain-free. Our first aim is to provide you with some active rest from pain-provoking activities. "No Pain. No Gain." does not apply in Sever's disease. If it hurts your child is doing too much exercise. Your child should reduce or cease any activity that causes heel pain. Ice is a simple and effective modality to reduce your pain and swelling. Please apply for 20-30 minutes each 2 to 4 hours during the initial phase or when you notice that your injury is warm or hot. Most children can tolerate paracetamol as a pain reducing medication. Check with your doctor. To support and protect your heels, you may need to be wear shock absorbing heel cups or a soft orthotic. Kinesio foot taping may help to provide pain relief.
Exercise
For children with Sever's disease, it is important to habitually perform exercises to stretch the hamstrings, calf muscles, and the tendons on the back of the leg. Stretching should be performed 2-3 times a day. Each stretch should be performed for 20 seconds, and both legs should be stretched, even if the pain is only in one heel. Heel cups or an inner shoe heel lifts are often recommended for patient suffering from Sever's disease. Wearing running shoes with built in heel cups can also decrease the symptoms because they can help soften the impact on the heel when walking, running, or standing.
Sever?s Disease (calcaneal aphophysitis) is not really a disease, but more a repetitious strain injury. This is the most common cause of kids heel pain seen at Podiatry Care. Active children in football, soccer, basketball, netball and tennis with this type of foot pain complain of pain in the region of the heel bone particularly after exercise. In severe cases, children will complain of pain during exercise as well. It is a frequent cause of heel pain in children, particularly in the very active child. It is most often seen in children between the ages of 8 to 15 years as the growth plate is not fully developed or calcified at this time.
Causes
Sever?s disease is most likely to occur during the growth spurt that occurs in adolescence. For girls, growth spurts usually occurs between 8 and 13 years of age. For boys, it?s typically between 10 and 15 years of age. The back of the heel hardens and becomes stronger when it finishes growing, which is why Sever?s rarely occurs in older adolescents and teenagers.
Symptoms
Sever's Disease is most commonly seen in physically active girls and boys from ages 10 to 15 years old. These are the years when the growth plate is still ""open,"" and has not fused into mature bone. Also, these are the years when the growth plate is most vulnerable to overuse injuries, which are usually caused by sports activities. The most common symptoms of this disease include. Heel pain in one or both heels. Usually seen in physically active children, especially at the beginning of a new sports season. The pain is usually experienced at the back of the heel, and includes the following areas. The back of the heel (that area which rubs against the back of the shoe). The sides of the heel. Actually, this is one of the diagnostic tests for Sever's Disease, squeezing the rear portion of the heel from both sides at the same time will produce pain. It is known as the Squeeze Test.
Diagnosis
A Podiatrist can easily evaluate your child?s foot, lower limbs and muscular flexibility, to identify if a problem exists. If a problem is identified, a simple treatment plan is put in place. Initial treatment may involve using temporary padding and strapping to control motion or to cushion the painful area and based on the success of this treatment, a long-term treatment plan will be put in place. This long-term treatment plan may or may not involve Foot Supports, Heel Raises, muscle stretching and or strengthening.
Non Surgical Treatment
Sever?s disease treatment should be based on eliminating pain and restoring normal foot and leg biomechanics. As with most soft tissue injuries the initial treatment is Rest, Ice, and Protect. In the early phase you?ll most likely be unable to walk pain-free. Our first aim is to provide you with some active rest from pain-provoking activities. "No Pain. No Gain." does not apply in Sever's disease. If it hurts your child is doing too much exercise. Your child should reduce or cease any activity that causes heel pain. Ice is a simple and effective modality to reduce your pain and swelling. Please apply for 20-30 minutes each 2 to 4 hours during the initial phase or when you notice that your injury is warm or hot. Most children can tolerate paracetamol as a pain reducing medication. Check with your doctor. To support and protect your heels, you may need to be wear shock absorbing heel cups or a soft orthotic. Kinesio foot taping may help to provide pain relief.
Exercise
For children with Sever's disease, it is important to habitually perform exercises to stretch the hamstrings, calf muscles, and the tendons on the back of the leg. Stretching should be performed 2-3 times a day. Each stretch should be performed for 20 seconds, and both legs should be stretched, even if the pain is only in one heel. Heel cups or an inner shoe heel lifts are often recommended for patient suffering from Sever's disease. Wearing running shoes with built in heel cups can also decrease the symptoms because they can help soften the impact on the heel when walking, running, or standing.
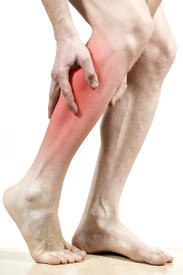

 Complete Achilles tendon ruptures occur most commonly at the mid-substance, but also distally at the insertion site or proximally at the myotendinous junction. These can be traumatic and devastating injuries, resulting in significant pain, disability, and healthcare cost. As many as 2.5 million individuals sustain Achilles tendon ruptures each year and the incidence is rising. This trend is due, in part, to an increase in athletic participation across individuals of all ages. Causes Repeated stress from a variety of causes is often the cause of Achilles tendon injury. The stress may occur from any of the following. Excessive activity or overuse. Flat feet. Poorly fitting or inadequate shoes. Inadequate warm-up or proper conditioning. Jogging or running on hard surfaces. Older recreational athlete. Previous Achilles tendon injury (tendonitis/rupture). Repeated steroid injections. Sudden changes in intensity of exercise. Use of fluoroquinolone antibiotics (especially in children). Trauma to the ankle. Tense calf muscles prior to exercise. Weak calf muscles. Symptoms Often the person feels a whip-like blow that is followed by weakness in the affected leg - usually he or she is not able to walk afterwards. At place where the tendon ruptured, a significant dent is palpable. Often the experienced physician can diagnose a ruptured Achilles tendon by way of clinical examination and special function tests. Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allow for a more precise diagnosis. Diagnosis In diagnosing an Achilles tendon rupture, the foot and ankle surgeon will ask questions about how and when the injury occurred and whether the patient has previously injured the tendon or experienced similar symptoms. The surgeon will examine the foot and ankle, feeling for a defect in the tendon that suggests a tear. Range of motion and muscle strength will be evaluated and compared to the uninjured foot and ankle. If the Achilles tendon is ruptured, the patient will have less strength in pushing down (as on a gas pedal) and will have difficulty rising on the toes. The diagnosis of an Achilles tendon rupture is typically straightforward and can be made through this type of examination. In some cases, however, the surgeon may order an MRI or other advanced imaging tests. Non Surgical Treatment Achilles tendon rupture is treated using non surgical method or surgical method. Non surgical treatment involves wearing a cast or special brace which is changed after some period of time to bring the tendon back to its normal length. Along with cast or brace, physical therapy may be recommended to improve the strength and flexibility of leg muscles and Achilles tendon.
Complete Achilles tendon ruptures occur most commonly at the mid-substance, but also distally at the insertion site or proximally at the myotendinous junction. These can be traumatic and devastating injuries, resulting in significant pain, disability, and healthcare cost. As many as 2.5 million individuals sustain Achilles tendon ruptures each year and the incidence is rising. This trend is due, in part, to an increase in athletic participation across individuals of all ages. Causes Repeated stress from a variety of causes is often the cause of Achilles tendon injury. The stress may occur from any of the following. Excessive activity or overuse. Flat feet. Poorly fitting or inadequate shoes. Inadequate warm-up or proper conditioning. Jogging or running on hard surfaces. Older recreational athlete. Previous Achilles tendon injury (tendonitis/rupture). Repeated steroid injections. Sudden changes in intensity of exercise. Use of fluoroquinolone antibiotics (especially in children). Trauma to the ankle. Tense calf muscles prior to exercise. Weak calf muscles. Symptoms Often the person feels a whip-like blow that is followed by weakness in the affected leg - usually he or she is not able to walk afterwards. At place where the tendon ruptured, a significant dent is palpable. Often the experienced physician can diagnose a ruptured Achilles tendon by way of clinical examination and special function tests. Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allow for a more precise diagnosis. Diagnosis In diagnosing an Achilles tendon rupture, the foot and ankle surgeon will ask questions about how and when the injury occurred and whether the patient has previously injured the tendon or experienced similar symptoms. The surgeon will examine the foot and ankle, feeling for a defect in the tendon that suggests a tear. Range of motion and muscle strength will be evaluated and compared to the uninjured foot and ankle. If the Achilles tendon is ruptured, the patient will have less strength in pushing down (as on a gas pedal) and will have difficulty rising on the toes. The diagnosis of an Achilles tendon rupture is typically straightforward and can be made through this type of examination. In some cases, however, the surgeon may order an MRI or other advanced imaging tests. Non Surgical Treatment Achilles tendon rupture is treated using non surgical method or surgical method. Non surgical treatment involves wearing a cast or special brace which is changed after some period of time to bring the tendon back to its normal length. Along with cast or brace, physical therapy may be recommended to improve the strength and flexibility of leg muscles and Achilles tendon.  Surgical Treatment Most published reports on surgical treatment fall into 3 different surgical approach categories that include the following: direct open, minimally invasive, and percutaneous. In multiple studies surgical treatment has demonstrated a lower rate of re-rupture compared to nonoperative treatment, but surgical treatment is associated with a higher rate of wound healing problems, infection, postoperative pain, adhesions, and nerve damage. Most commonly the direct open approach involves a 10- to 18-cm posteromedial incision. The minimally invasive approach has a 3- to 10-cm incision, and the percutaneous approach involves repairing the tendon through multiple small incisions. As with nonsurgical treatment there exists wide variation in the reported literature regarding postoperative treatment protocols. Multiple comparative studies have been published comparing different surgical approaches, repair methods, or postoperative treatment protocols.
Surgical Treatment Most published reports on surgical treatment fall into 3 different surgical approach categories that include the following: direct open, minimally invasive, and percutaneous. In multiple studies surgical treatment has demonstrated a lower rate of re-rupture compared to nonoperative treatment, but surgical treatment is associated with a higher rate of wound healing problems, infection, postoperative pain, adhesions, and nerve damage. Most commonly the direct open approach involves a 10- to 18-cm posteromedial incision. The minimally invasive approach has a 3- to 10-cm incision, and the percutaneous approach involves repairing the tendon through multiple small incisions. As with nonsurgical treatment there exists wide variation in the reported literature regarding postoperative treatment protocols. Multiple comparative studies have been published comparing different surgical approaches, repair methods, or postoperative treatment protocols.
 Rupture of Achilles tendon is the most common among those taking place in the lower extremities, being twice as common in men than in women between 30-50 years old and usually caused while doing sport. There are some risk factors such as age or chronic treatments based on corticosteroids or antibiotics when belonging to Quinolones group. Spontaneous bilateral rupture of the Achilles tendon is much more infrequent, being almost exceptional in young and healthy patients without known pathological conditions.
Rupture of Achilles tendon is the most common among those taking place in the lower extremities, being twice as common in men than in women between 30-50 years old and usually caused while doing sport. There are some risk factors such as age or chronic treatments based on corticosteroids or antibiotics when belonging to Quinolones group. Spontaneous bilateral rupture of the Achilles tendon is much more infrequent, being almost exceptional in young and healthy patients without known pathological conditions.
