Overview
Limb deformity or leg length problems can be treated by applying an external frame to the leg. The frame consists of metal rings which go round the limb. The rings are held onto the body by wires and metal pins which pass through the skin and are anchored into the bone. During this operation, the bone is divided. Gradual adjustment of the frame results in creation of a new bone allowing a limb to be lengthened. The procedure involves the child having an anaesthetic. The child is normally in hospital for one week. The child and family are encouraged to clean pin sites around the limb. The adjustments of the frame (distractions) are performed by the child and/or family. The child is normally encouraged to walk on the operated limb and to actively exercise the joints above and below the frame. The child is normally reviewed on a weekly basis in clinic to monitor the correction of the deformity. The frame normally remains in place for 3 months up to one year depending on the condition which is being treated. The frame is normally removed under a general anaesthetic at the end of treatment.
Causes
Sometimes the cause of LLD is unknown, yet the pattern or combination of conditions is consistent with a certain abnormality. Examples include underdevelopment of the inner or outer side of the leg (hemimelias) or (partial) inhibition of growth of one side of the body of unknown cause (hemihypertrophy). These conditions are present at birth, but the limb length difference may be too small to be detected. As the child grows, the LLD increases and becomes more noticeable. In hemimelia, one of the two bones between the knee and the ankle (tibia or fibula) is abnormally short. There also may be associated foot or knee abnormalities. Hemihypertrophy or hemiatrophy are rare conditions in which there is a difference in length of both the arm and leg on only one side of the body. There may also be a difference between the two sides of the face. Sometimes no cause can be found. This type of limb length is called idiopathic. While there is a cause, it cannot be determined using currect diagnostic methods.
Symptoms
Back pain along with pain in the foot, knee, leg and hip on one side of the body are the main complaints. There may also be limping or head bop down on the short side or uneven arm swinging. The knee bend, hip or shoulder may be down on one side, and there may be uneven wear to the soles of shoes (usually more on the longer side).
Diagnosis
There are several orthopedic tests that are used, but they are rudimentary and have some degree of error. Even using a tape measure with specific anatomic landmarks has its errors. Most leg length differences can be seen with a well trained eye, but I always recommend what is called a scanagram, or a x-ray bone length study (see picture above). This test will give a precise measurement in millimeters of the length difference.
Non Surgical Treatment
In some circumstances, the physician will recommend a non-surgical form of treatment. Non-surgical treatments include orthotics and prosthetics. Orthotics are a special type of lift placed in or on a shoe that can be used in the treatment of leg length discrepancies between two and six centimeters. In pediatric patients who have large discrepancies and are not good candidates for other treatment forms, prosthetics can be helpful.

how to increase height in 1 week
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is another option. In some cases the longer extremity can be shortened, but a major shortening may weaken the muscles of the extremity. In growing children, lower extremities can also be equalized by a surgical procedure that stops the growth at one or two sites of the longer extremity, while leaving the remaining growth undisturbed. Your physician can tell you how much equalization can be attained by surgically halting one or more growth centers. The procedure is performed under X-ray control through very small incisions in the knee area. This procedure will not cause an immediate correction in length. Instead, the LLD will gradually decrease as the opposite extremity continues to grow and "catch up." Timing of the procedure is critical; the goal is to attain equal length of the extremities at skeletal maturity, usually in the mid- to late teens. Disadvantages of this option include the possibility of slight over-correction or under-correction of the LLD and the patient?s adult height will be less than if the shorter extremity had been lengthened. Correction of significant LLDs by this method may make a patient?s body look slightly disproportionate because of the shorter legs.
Limb deformity or leg length problems can be treated by applying an external frame to the leg. The frame consists of metal rings which go round the limb. The rings are held onto the body by wires and metal pins which pass through the skin and are anchored into the bone. During this operation, the bone is divided. Gradual adjustment of the frame results in creation of a new bone allowing a limb to be lengthened. The procedure involves the child having an anaesthetic. The child is normally in hospital for one week. The child and family are encouraged to clean pin sites around the limb. The adjustments of the frame (distractions) are performed by the child and/or family. The child is normally encouraged to walk on the operated limb and to actively exercise the joints above and below the frame. The child is normally reviewed on a weekly basis in clinic to monitor the correction of the deformity. The frame normally remains in place for 3 months up to one year depending on the condition which is being treated. The frame is normally removed under a general anaesthetic at the end of treatment.

Causes
Sometimes the cause of LLD is unknown, yet the pattern or combination of conditions is consistent with a certain abnormality. Examples include underdevelopment of the inner or outer side of the leg (hemimelias) or (partial) inhibition of growth of one side of the body of unknown cause (hemihypertrophy). These conditions are present at birth, but the limb length difference may be too small to be detected. As the child grows, the LLD increases and becomes more noticeable. In hemimelia, one of the two bones between the knee and the ankle (tibia or fibula) is abnormally short. There also may be associated foot or knee abnormalities. Hemihypertrophy or hemiatrophy are rare conditions in which there is a difference in length of both the arm and leg on only one side of the body. There may also be a difference between the two sides of the face. Sometimes no cause can be found. This type of limb length is called idiopathic. While there is a cause, it cannot be determined using currect diagnostic methods.
Symptoms
Back pain along with pain in the foot, knee, leg and hip on one side of the body are the main complaints. There may also be limping or head bop down on the short side or uneven arm swinging. The knee bend, hip or shoulder may be down on one side, and there may be uneven wear to the soles of shoes (usually more on the longer side).
Diagnosis
There are several orthopedic tests that are used, but they are rudimentary and have some degree of error. Even using a tape measure with specific anatomic landmarks has its errors. Most leg length differences can be seen with a well trained eye, but I always recommend what is called a scanagram, or a x-ray bone length study (see picture above). This test will give a precise measurement in millimeters of the length difference.
Non Surgical Treatment
In some circumstances, the physician will recommend a non-surgical form of treatment. Non-surgical treatments include orthotics and prosthetics. Orthotics are a special type of lift placed in or on a shoe that can be used in the treatment of leg length discrepancies between two and six centimeters. In pediatric patients who have large discrepancies and are not good candidates for other treatment forms, prosthetics can be helpful.

how to increase height in 1 week
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is another option. In some cases the longer extremity can be shortened, but a major shortening may weaken the muscles of the extremity. In growing children, lower extremities can also be equalized by a surgical procedure that stops the growth at one or two sites of the longer extremity, while leaving the remaining growth undisturbed. Your physician can tell you how much equalization can be attained by surgically halting one or more growth centers. The procedure is performed under X-ray control through very small incisions in the knee area. This procedure will not cause an immediate correction in length. Instead, the LLD will gradually decrease as the opposite extremity continues to grow and "catch up." Timing of the procedure is critical; the goal is to attain equal length of the extremities at skeletal maturity, usually in the mid- to late teens. Disadvantages of this option include the possibility of slight over-correction or under-correction of the LLD and the patient?s adult height will be less than if the shorter extremity had been lengthened. Correction of significant LLDs by this method may make a patient?s body look slightly disproportionate because of the shorter legs.




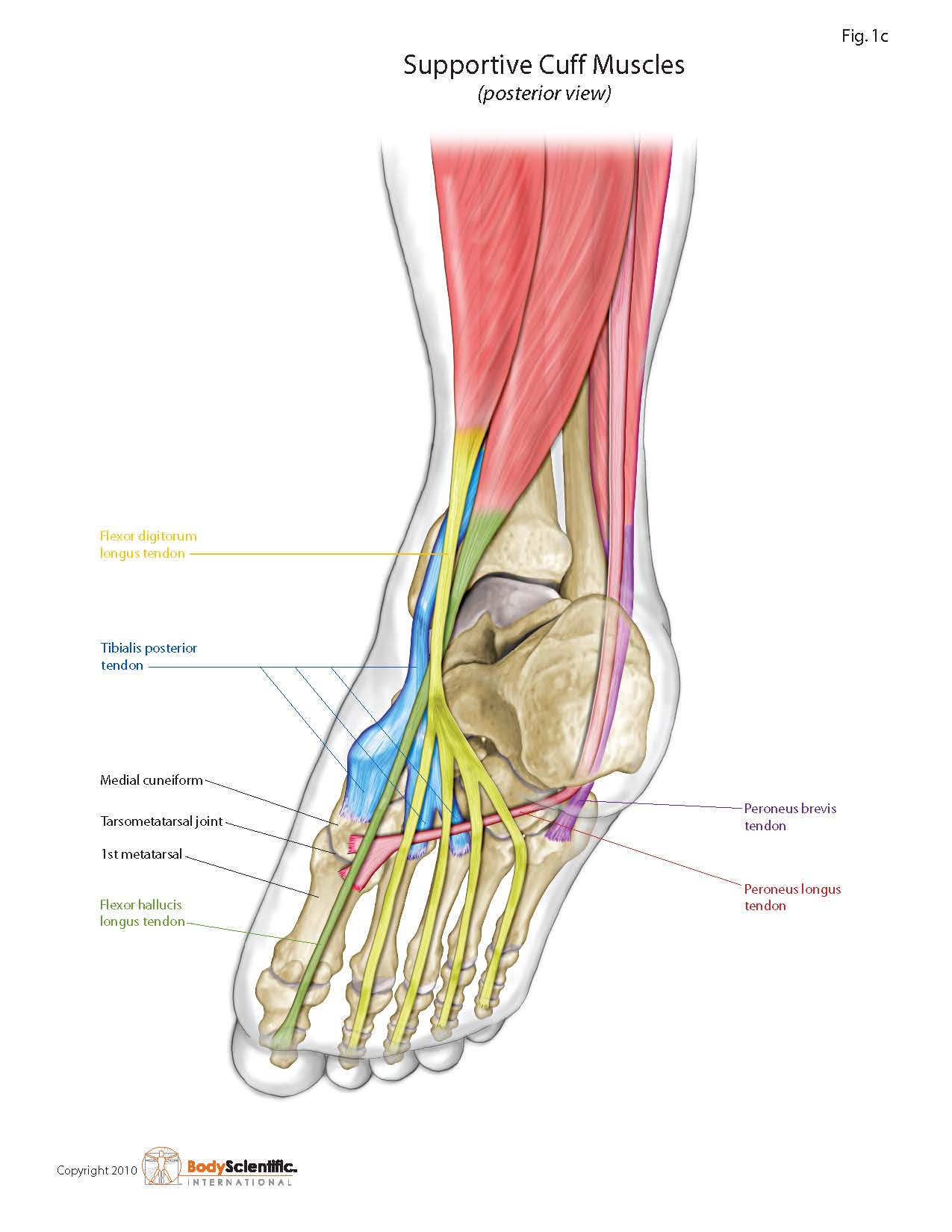
.jpg) Morton's neuroma is named after Dr Morton who first described this condition in 1876. It is sometimes called Morton's metatarsalgia or interdigital neuroma. It is a condition that affects one of the common plantar digital nerves that run between the long bones (metatarsals) in the foot. It most commonly affects the nerve between the third and fourth metatarsal bones, causing pain and numbness in the third and fourth toes. It can also affect the nerve between the second and third metatarsal bones, causing symptoms in the second and third toes. Morton's neuroma rarely affects the nerve between the first and second, or between the fourth and fifth, metatarsal bones. It tends to affect only one foot. It is rare to get two neuromas at the same time in the same foot.
Morton's neuroma is named after Dr Morton who first described this condition in 1876. It is sometimes called Morton's metatarsalgia or interdigital neuroma. It is a condition that affects one of the common plantar digital nerves that run between the long bones (metatarsals) in the foot. It most commonly affects the nerve between the third and fourth metatarsal bones, causing pain and numbness in the third and fourth toes. It can also affect the nerve between the second and third metatarsal bones, causing symptoms in the second and third toes. Morton's neuroma rarely affects the nerve between the first and second, or between the fourth and fifth, metatarsal bones. It tends to affect only one foot. It is rare to get two neuromas at the same time in the same foot.






 Overview
Overview Symptoms
Symptoms Prevention
Prevention